Introducing the empirical molecular formula practice worksheet, an invaluable tool for mastering the fundamental concepts of empirical molecular formulas. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of empirical molecular formulas, providing a thorough understanding and equipping you with practical problem-solving skills.
Through engaging explanations, detailed examples, and a variety of practice problems, this worksheet empowers you to confidently determine empirical molecular formulas, unravel their limitations, and explore their wide-ranging applications.
Empirical Molecular Formula: Empirical Molecular Formula Practice Worksheet

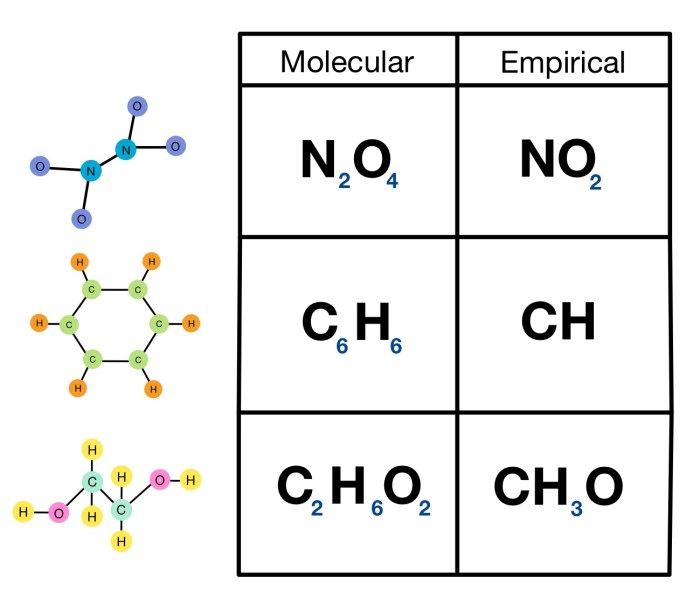
An empirical molecular formula is a chemical formula that represents the simplest whole-number ratio of the atoms in a compound. It does not specify the structure of the compound, only the relative number of each type of atom present.
For example, the empirical molecular formula of glucose is CH 2O. This means that for every carbon atom in a glucose molecule, there are two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. However, the empirical molecular formula does not tell us anything about the structure of the glucose molecule, such as how the atoms are bonded together.
Limitations of Empirical Molecular Formulas, Empirical molecular formula practice worksheet
Empirical molecular formulas have some limitations. They do not provide any information about the structure of a compound, and they can be ambiguous for compounds that have the same empirical formula but different structures. For example, both glucose and fructose have the same empirical molecular formula, CH 2O, but they have different structures.
Practice Worksheet
This practice worksheet includes a variety of empirical molecular formula problems. To complete the worksheet, you will need to determine the empirical molecular formula of each compound based on the given information.
- A compound is composed of 40.0% carbon, 6.7% hydrogen, and 53.3% oxygen by mass. What is the empirical molecular formula of the compound?
- A compound contains 2.1 g of hydrogen, 16.0 g of carbon, and 32.0 g of oxygen. What is the empirical molecular formula of the compound?
- A compound has a molar mass of 60.0 g/mol and is composed of 50.0% carbon, 41.7% hydrogen, and 8.3% oxygen by mass. What is the empirical molecular formula of the compound?
Key:
- CH2O
- CH 4O
- C 2H 6O
Applications of Empirical Molecular Formulas

Empirical molecular formulas have a variety of applications in chemistry, biology, and medicine. They can be used to:
- Identify compounds
- Determine the molar mass of a compound
- Calculate the percentage composition of a compound
- Predict the chemical properties of a compound
- Develop new drugs and materials
Advanced Topics
More advanced topics related to empirical molecular formulas include:
- Molecular weight determination
- Structural analysis
- Isotope analysis
These topics are discussed in more detail in advanced chemistry and biochemistry courses.
FAQ Insights
What is an empirical molecular formula?
An empirical molecular formula represents the simplest whole-number ratio of elements present in a compound, indicating the relative proportions of each element but not necessarily the actual molecular structure.
How do I determine the empirical molecular formula of a compound?
To determine the empirical molecular formula, you need to know the mass percentages or moles of each element in the compound. Then, convert these values to mole ratios, divide by the smallest mole ratio, and simplify to obtain the whole-number ratio.
What are the limitations of empirical molecular formulas?
Empirical molecular formulas do not provide information about the molecular structure or the arrangement of atoms within the molecule. They only indicate the relative proportions of elements.
