The intraoral technique of exposing dental images offers a vital means of capturing detailed visualizations of the oral cavity, aiding in the diagnosis and treatment of dental conditions. This technique involves the placement of an imaging device within the patient’s mouth to obtain clear and accurate images of the teeth, gums, and surrounding structures.
Intraoral imaging encompasses a range of techniques, including bitewing radiography, periapical radiography, and panoramic radiography. Each technique employs specific exposure parameters and utilizes specialized equipment to capture images from different angles and perspectives. The choice of technique depends on the specific diagnostic needs and clinical requirements.
Intraoral Imaging Techniques: Intraoral Technique Of Exposing Dental Images
Intraoral imaging techniques provide a non-invasive method of visualizing the internal structures of the oral cavity. These techniques include:
- Bitewing radiography:Used to visualize the crowns and roots of teeth in the upper and lower jaws.
- Periapical radiography:Used to visualize the entire tooth, including the root tip and surrounding bone.
- Occlusal radiography:Used to visualize the floor of the mouth and the palate.
- Panoramic radiography:Used to visualize the entire jaw and teeth in a single image.
- Cone beam computed tomography (CBCT):Used to create three-dimensional images of the jaw and teeth.
Each technique has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of technique depends on the specific clinical situation.
Patient Preparation
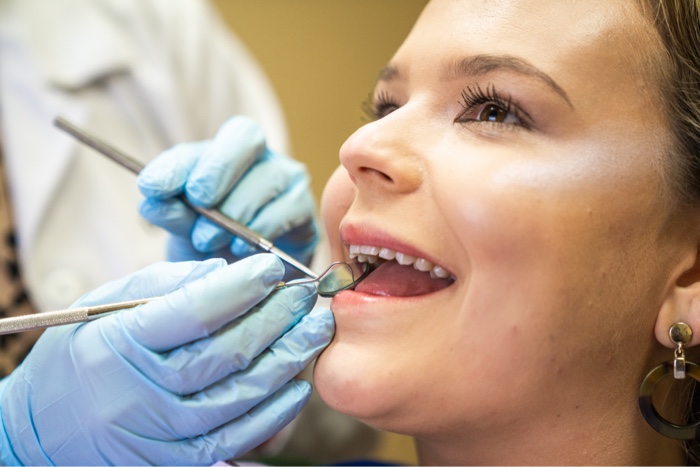
Proper patient preparation is essential for successful intraoral imaging. This includes:
- Explaining the procedure to the patient and obtaining informed consent.
- Positioning the patient correctly in the dental chair.
- Using bitewings or other patient aids to stabilize the film or sensor.
- Ensuring that the patient remains still during the exposure.
Patient cooperation is essential for obtaining high-quality images.
Image Acquisition
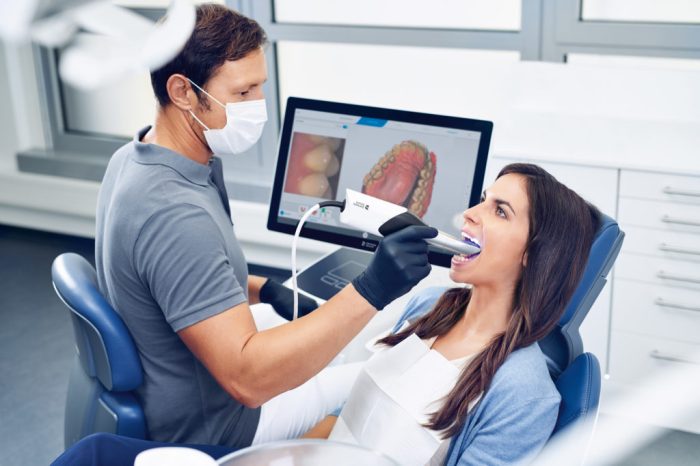
Image acquisition involves the following steps:
- Selecting the appropriate exposure parameters (kVp, mA, time).
- Positioning the X-ray beam perpendicular to the film or sensor.
- Exposing the film or sensor to the X-ray beam.
- Processing the film or digital image.
Proper exposure parameters are essential for obtaining images with optimal contrast and detail.
Image Processing
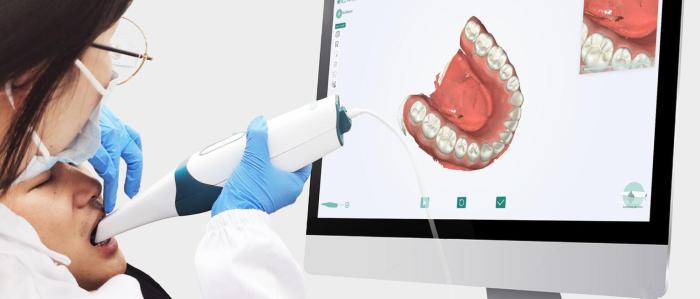
Image processing techniques can be used to enhance the visibility of anatomical structures and improve the diagnostic value of intraoral images. These techniques include:
- Contrast enhancement:Adjusts the contrast between different shades of gray to make anatomical structures more visible.
- Edge enhancement:Sharpens the edges of anatomical structures to improve their definition.
- Noise reduction:Removes random noise from the image to improve its clarity.
Image processing can be performed manually or using software tools.
Common Queries
What are the advantages of intraoral imaging?
Intraoral imaging offers numerous advantages, including the ability to capture detailed images of the oral cavity, aiding in the diagnosis and treatment planning of dental conditions. It allows for the detection of caries, periodontal disease, and other abnormalities that may not be visible during a visual examination.
How does intraoral imaging ensure patient safety?
Intraoral imaging is designed to minimize radiation exposure to patients. Modern digital sensors and imaging systems utilize low-dose radiation techniques, reducing the risk of potential harm. Additionally, protective measures such as lead aprons and thyroid shields are employed to further safeguard patients during imaging procedures.
What are the different types of intraoral imaging techniques?
There are several types of intraoral imaging techniques, including bitewing radiography, periapical radiography, and panoramic radiography. Bitewing radiography captures images of the crowns and interproximal surfaces of the teeth, while periapical radiography provides detailed views of the entire tooth and surrounding bone.
Panoramic radiography offers a comprehensive view of the entire dentition and jaw structures.