Correctly label the following lymphatics of the abdominal cavity – Correctly labeling the lymphatics of the abdominal cavity is essential for understanding the lymphatic drainage of this region and its clinical significance. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the superficial and deep lymphatic vessels of the abdominal cavity, their anatomical relationships, and their role in disease spread.
The lymphatic system plays a crucial role in maintaining fluid balance, transporting nutrients and waste products, and providing immune surveillance. In the abdominal cavity, the lymphatic vessels drain fluid and waste from the abdominal organs and abdominal wall. Understanding the lymphatic drainage patterns is important for surgical procedures, as well as for diagnosing and treating diseases that affect the abdominal cavity.
Lymphatic Drainage of the Abdominal Cavity
The lymphatic system plays a crucial role in maintaining fluid balance, removing waste products, and transporting immune cells throughout the body. The abdominal cavity, which houses various organs, has a complex network of lymphatic vessels that drain excess fluid and transport it to the lymph nodes for further processing.
Major Lymphatic Trunks and Their Drainage Areas
The abdominal cavity is drained by several major lymphatic trunks:
- Lumbar trunks:Drain the posterior abdominal wall, kidneys, and adrenal glands.
- Iliac trunks:Drain the pelvic organs, lower abdominal wall, and inguinal region.
- Celiac trunk:Drains the stomach, pancreas, liver, and spleen.
- Superior mesenteric trunk:Drains the small intestine and proximal colon.
- Inferior mesenteric trunk:Drains the distal colon and rectum.
Superficial Lymphatics of the Abdominal Cavity: Correctly Label The Following Lymphatics Of The Abdominal Cavity
The superficial lymphatics of the abdominal cavity drain the skin and subcutaneous tissues of the abdominal wall. These vessels are located in the superficial fascia and follow the course of the blood vessels.
Course and Termination
The superficial lymphatics of the abdominal cavity can be divided into three groups:
- Anterior group:Drains the skin and subcutaneous tissues of the anterior abdominal wall. The vessels ascend to the axillary lymph nodes.
- Lateral group:Drains the skin and subcutaneous tissues of the lateral abdominal wall. The vessels terminate in the inguinal lymph nodes.
- Posterior group:Drains the skin and subcutaneous tissues of the posterior abdominal wall. The vessels descend to the lumbar lymph nodes.
Deep Lymphatics of the Abdominal Cavity
The deep lymphatics of the abdominal cavity drain the abdominal organs and their associated structures. These vessels are located within the mesentery and follow the course of the blood vessels.
Anatomical Relationships and Drainage Patterns
The deep lymphatics of the abdominal cavity can be divided into two groups:
- Parietal lymphatics:Drain the parietal peritoneum and the structures attached to it.
- Visceral lymphatics:Drain the abdominal organs.
The parietal lymphatics form a network of vessels that follow the course of the abdominal blood vessels. The visceral lymphatics form plexuses around the abdominal organs and follow the course of the blood vessels within the mesentery.
Clinical Significance of Abdominal Lymphatics
The abdominal lymphatics play a significant role in the spread of disease. Tumor cells can spread through the lymphatic vessels to regional lymph nodes and distant organs.
Surgical Procedures, Correctly label the following lymphatics of the abdominal cavity
The lymphatic drainage of the abdominal cavity must be considered during surgical procedures. Dissection of the lymph nodes can disrupt lymphatic drainage and lead to lymphedema.
Imaging of Abdominal Lymphatics
Various imaging techniques can be used to visualize abdominal lymphatics. These techniques include:
Advantages and Limitations
- Lymphoscintigraphy:Involves the injection of a radioactive tracer into the lymphatic system. Advantages: Non-invasive, provides functional information about lymphatic drainage. Limitations: Radiation exposure, limited spatial resolution.
- Magnetic resonance lymphangiography (MRL):Uses magnetic resonance imaging to visualize lymphatic vessels. Advantages: Non-invasive, high spatial resolution. Limitations: Time-consuming, expensive.
- Computed tomography (CT) lymphangiography:Uses CT imaging to visualize lymphatic vessels. Advantages: Widely available, relatively inexpensive. Limitations: Radiation exposure, lower spatial resolution than MRL.
Popular Questions
What is the general pattern of lymphatic drainage from the abdominal cavity?
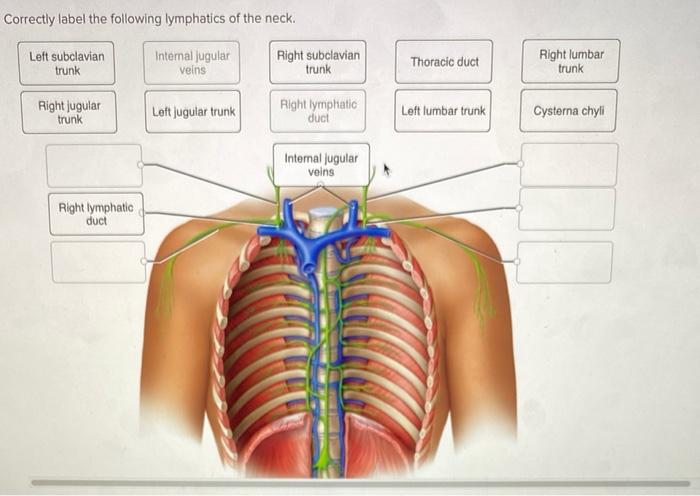
The lymphatic vessels of the abdominal cavity drain into the lumbar lymph nodes, which are located along the aorta and inferior vena cava. From the lumbar lymph nodes, the lymph flows into the cisterna chyli, which is a sac-like structure located at the level of the second lumbar vertebra.
The cisterna chyli then drains into the thoracic duct, which empties into the left subclavian vein.
What are the major lymphatic trunks of the abdominal cavity and what areas do they drain?
The major lymphatic trunks of the abdominal cavity are the lumbar trunks, the intestinal trunk, and the hepatic trunk. The lumbar trunks drain the posterior abdominal wall, the intestinal trunk drains the small and large intestines, and the hepatic trunk drains the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas.
What is the clinical significance of abdominal lymphatics?
Abdominal lymphatics play a role in the spread of disease, such as cancer. Cancer cells can enter the lymphatic vessels and travel to other parts of the body. Understanding the lymphatic drainage patterns is important for surgical procedures, as well as for diagnosing and treating diseases that affect the abdominal cavity.
